Hepatitis
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis literally translates to “Inflammation of the Liver”. Though a healthy liver has multiple functions, its most important function is to aid in digestion. Thus quite naturally, an ailing or
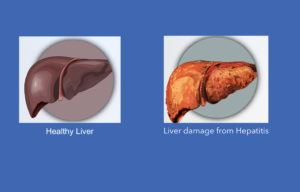
inflamed liver causes disruption in the digestive system. But not all digestive problems are linked to liver damage.
How did I get Hepatitis?
Hepatitis mostly occurs due to infections of the liver by different viruses. The disease duration and severity depends on the type of virus which has affected the liver. In India, the most common viruses to cause Hepatitis are:
- Hepatitis A Virus: The most common cause of jaundice, this virus enters the body through contaminated food or water. With proper care and medications, Hepatitis A patients can get cured within a few weeks, however a delay in diagnosis can have disastrous consequences and might even be fatal.
- Hepatitis B Virus: This virus enters the body through body fluids from an infected person; be it a blood donor or a mother during childbirth. Hepatitis B patients are chronic and the disease takes years to progress, but can lead to serious liver damage and even death.
- Hepatitis C Virus: Similar to Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C patients also get infected from body fluids of infected patients. The most common route of infection is the sharing of needles, particularly in illicit drug use. Though chronic in nature, Hepatitis C causes severe damage to the liver which can ultimately lead to Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma).
Apart from these viruses, physical trauma and overdose of some medicines can also cause Hepatitis.
When do I consult my doctor?
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Yellowish discoloration of skin and eyes
These are some of the tell-tale symptoms of Hepatitis. Consult your physician whenever you face any of these.
What are my treatment options?
The treatment of Hepatitis varies greatly with the cause, duration and extent of liver involvement. While some mild cases can be treated with oral medicines at home, serious cases often require hospitalization and ICU support. In some patients, the extent of liver damage is so severe that they might also require liver transplantation.
Like every disease, Hepatitis too is better prevented than cured. Eat and drink packaged food and beverages only, and avoid roadside food. For any blood donation camp, make sure needles are being disposed of immediately after use. Whenever you have any symptoms or even doubts regarding your liver, consult a physician at once.
About the Author

Dr. Abhijit Ray
- MBBS, MD (Int. Med.), ISHF, FACP, FRSM
- Holds Certificates from Johns Hopkins University
- Holds Certificates from Harvard Medical School
- Gold Medalist Advanced ECG Interpretation American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine